Orchids are some of the most exotic plants on earth. They display an amazing range of diversity in the size, shape and color of their unique flowers. There is a misconception, however, that these floral treasures are difficult to grow, when in fact more and more gardeners are growing and collecting orchids each year. Provide the essentials of good care and you too can grow orchids easily!
Growing Orchids
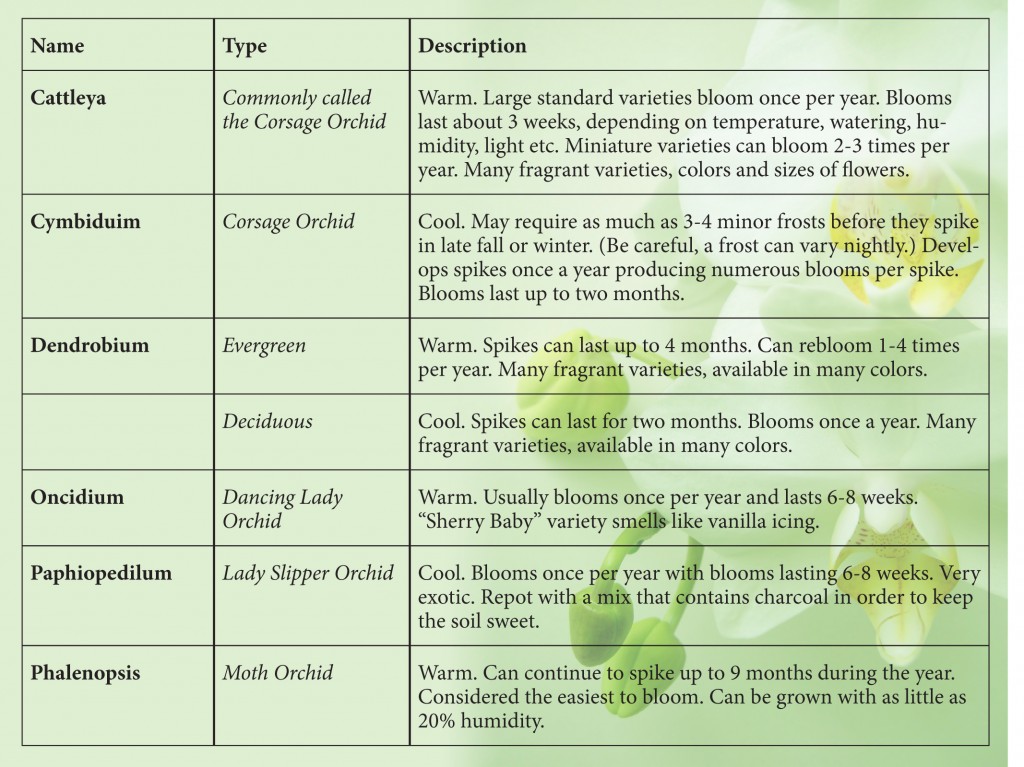
Orchids have some unique needs when it comes to proper care. Because they can be temperamental at times, it is best to carefully investigate the types of orchids you are interested in growing and be sure you can meet their individual needs.
- Light: Most orchids prefer abundant, filtered sunlight. This can be met with west- or south-facing windows, or you may need some supplemental light sources. A few popular orchid varieties can grow in lower light levels.
- Temperature: Like any plants, orchids can do well in a temperature range, though some prefer warmer locations and some prefer cooler locations. Measure the temperature range where you want to grow orchids and select varieties that will do well in that range.
- Humidity: Orchids are tropical plants that do well in more humid environments. They can do well in terrariums or greenhouses where the humidity can be elevated, or you can take steps to increase the humidity around the orchids in your home, such as through plant grouping, pebble trays or misting.
- Watering: Orchids tend to do best if they dry out somewhat between thorough waterings. Plant your orchids in an appropriate medium, and take great care with watering so they can absorb sufficient moisture without fostering root rot or other mildew.
- Fertilizing: Fertilizers are not critical for blooming orchids, but they can help provide better nourishment. Fertilizing lightly is better than over-fertilizing, and fertilizer should only be applied during active growth periods.
The exact care your orchids will need will depend on the varieties you choose. Research their optimal environments and you’ll be well prepared to host an array of stunning orchids in your home.
Common Orchid Varieties and Care